
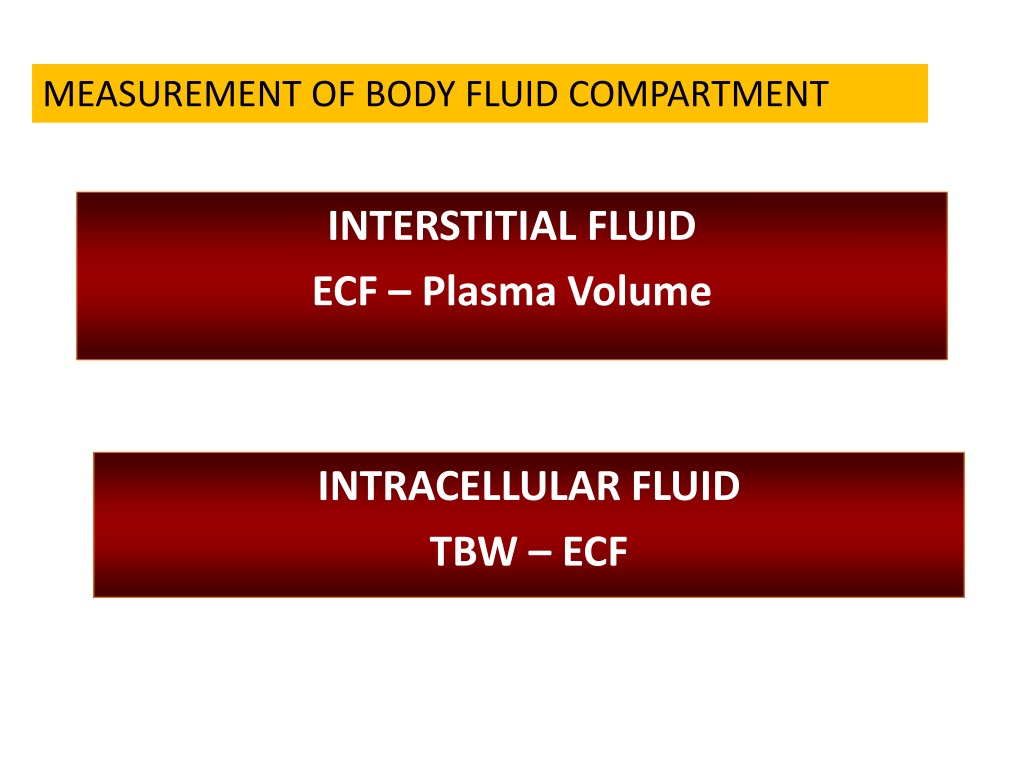
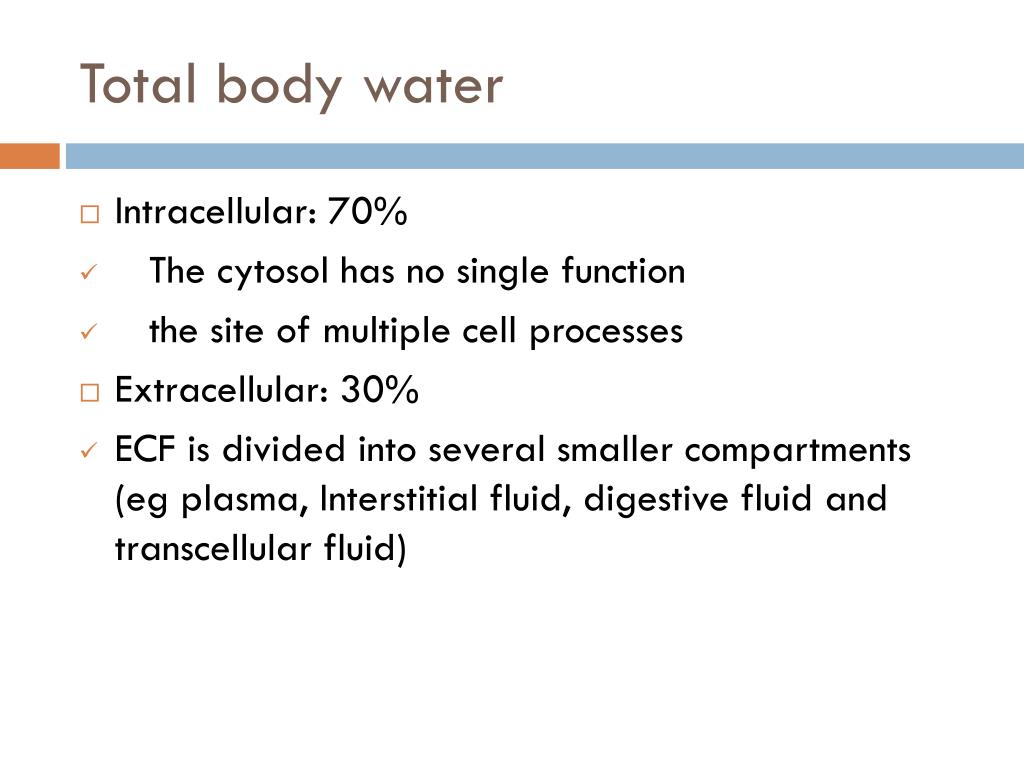
So for example, the K+ in the intracellular fluid is balanced out by negatively charged proteins and organic phosphates. The major intracellular cations are potassium (K+) and magnesium (Mg2+), whereas the major anions are proteins and organic phosphates like ATP.įluid compartments always maintain the same concentration of positive charges as negative ones in order to stay electrically neutral - that’s called the principle of macroscopic electroneutrality. Intracellular fluid is important for dissolving cations which are molecules with a positive charge, and anions which are molecules with a negative charge. Total body water can be subdivided into two major compartments, intracellular fluid which is fluid inside cells, and extracellular fluid which is fluid outside of cell like in the blood and in the interstitial tissue between cells.Īssuming that the total body water is about 60% of their body weight, roughly 2/3 of that, or 40% is intracellular fluid, and the other 1/3 or 20% is extracellular fluid.

So a really muscular and lean person would have a relatively high proportion of their body weight made up of water.Īdditionally, females tend to have more fat than males and so on average tend to have lower proportion of their body weight made up of water. Since fat doesn’t store any water, a person’s water content is inversely proportional to a person’s fat content.
Water is the key to life, and it takes up a big proportion of our body weight, typically around 60 percent! The precise amount of water depends on a person’s body composition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
